For industries like Life Sciences, it is challenging to collect a large amount of data with high quality that is needed for machine learning and autonomous control applications.
Instead, we settle with simulations where initial research and experiments can be conducted. However, it is often difficult to create a high-fidelity simulation for biopharma processes. To make it worse, these good simulations, when they do exist, are often not open-sourced.
Fortunately, there is this great project that offers the mechanistic model, implementation, and sample production runs. It is a realistic simulation of industrial-scale fed-batch penicillin fermentation.
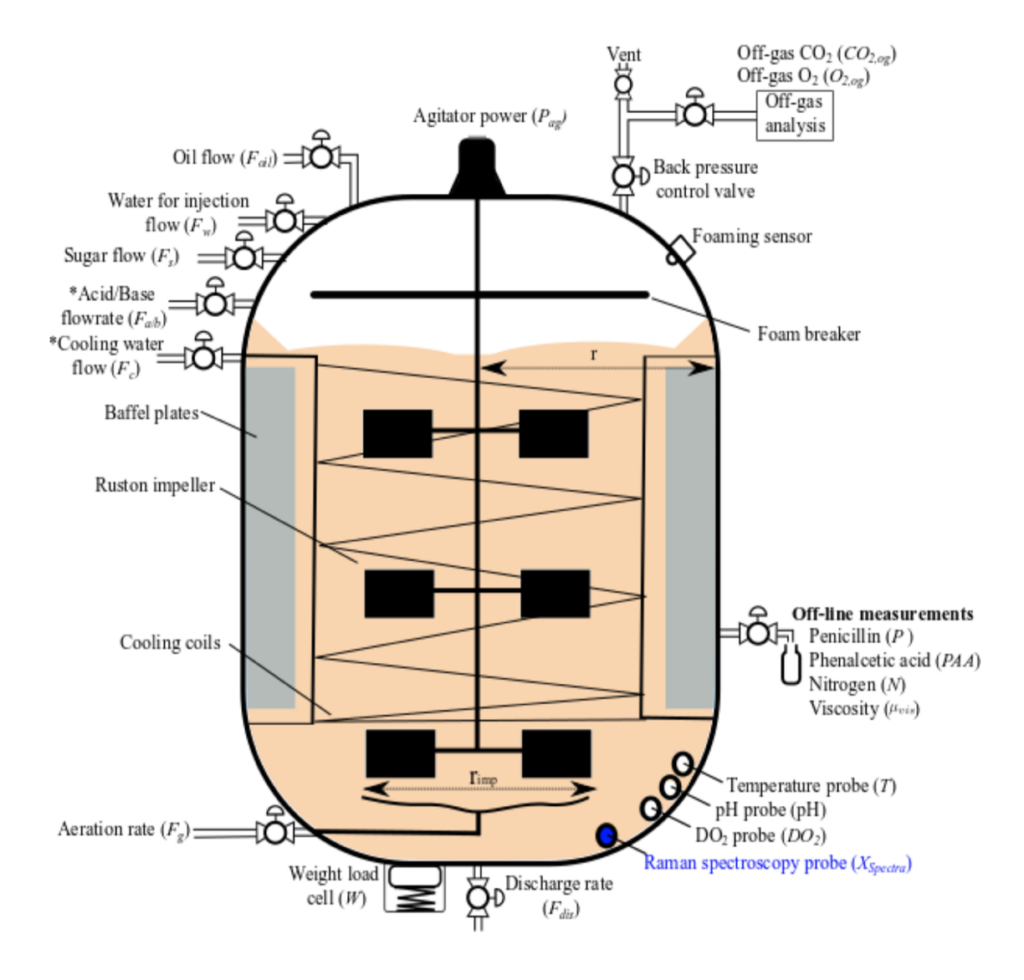
The bioreactor simulation adapts a peer-reviewed mathematical structure model to describe penicillin fermentation with the inclusion of the main environmental effects (e.g. dissolved oxygen, viscosity, temperature, pH, and dissolved carbon dioxide).
There are automatically controlled variables (e.g. temperature and pH) that are regulated using a feed-back PID loop, as well as manually controlled variables (e.g. substrate flowrate, phenylacetic acid flowrate) that are manipulated via setpoints (e.g. using a recipe-driven approach).
To take it a step further, the Quartic AI team built its own version to better accommodate the research needs:
- Python Implementation – Python is the most popular language in the AI community so having a Python implementation is necessary to conduct frontier AI research.
- Custom C++ ODE Solver – While we were able to rewrite everything in Python we weren’t particularly satisfied with the simulation speed (around 30-40s* per batch for Python and MATLAB implementations ).
Failing to find efficient and reliable open-source ODE solvers, we implemented our own. Currently, we are looking at around 1s per batch by integrating our C++ ODE solver.
- More consistent API – One of the most popular toolkits for testing different control or Reinforcement Learning algorithms is OpenAI Gym Environment. Therefore, it is beneficial to have this simulation environment to have similar APIs.
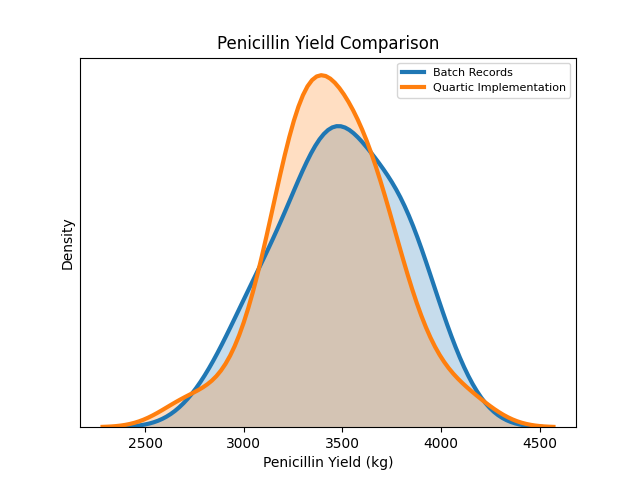
To assess the accuracy of the simulation, we compared simulation outputs with the actual offline batch records. From the chart, we observe that our implementation produces very similar outcomes as the batch records.
We have conducted successful R&D projects internally and would like to open-source this so it could be helpful to our community. Please reach out if you are interested in what we do and feel free to contribute to the GitHub repos!